What Is Prenatal Care, And Why Is It Important?
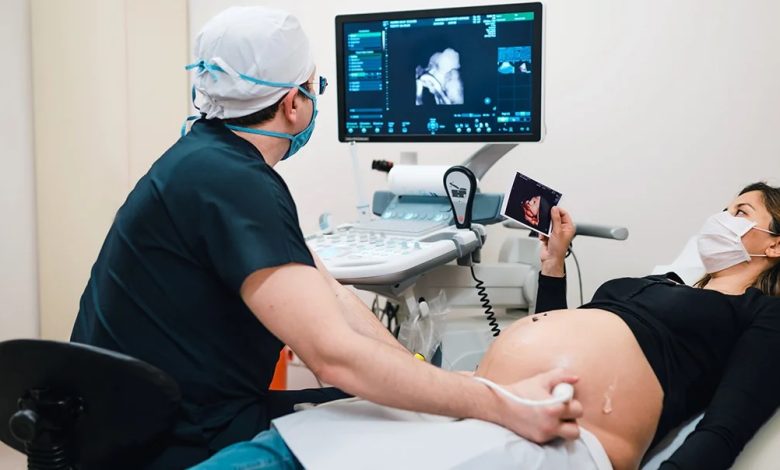
Pregnancy is a physiological stage during which the maternal body transforms to give birth to a new being. Although it is a natural process, it is not without complications. To prevent them, there are a series of prenatal care that the pregnant woman should not ignore.
In this care, periodic medical check-ups in Unity Screen for example allow early detection of risky situations that could compromise the mother’s or baby’s health. What are they, and why are they important at each stage of pregnancy?
The Importance Of Prenatal Care
Prenatal care aims to improve or maintain the health of the mother and baby during pregnancy and know that Only UNITY screens your baby’s risk for bad conditions without needing a paternal sample. They are carried out through periodic medical evaluations. The frequency of which increases as the pregnancy progresses. During prenatal examinations, health care is established through the following strategies:
- Prevention, diagnosis, and rapid treatment of pregnancy complications.
- Monitoring of baby’s growth and vitality.
- Education of women and their families on birth and postpartum issues.
- Treatment of typical symptoms or discomforts of pregnancy.
- Preparation of the pregnant woman for the birth of the baby.
Babies born to mothers who did not receive adequate prenatal care can suffer from various health complications. These children are estimated to triple the risk of low birth weight compared to children of mothers who attended all checks. In addition, they are five times more likely to die than the latter.
On the other hand, the WHO states that antenatal care of at least 8 visits can reduce perinatal deaths by up to 8 in 1000 births. In this sense, prenatal care can prevent pregnancy, childbirth, and postpartum complications. Prenatal visits also help pregnant women live more peacefully during pregnancy. And to prepare physically and psychologically for what awaits them.
Fetal Ultrasound
This complimentary examination is used to observe the baby inside the uterus and corroborate its adequate growth, among other things. In general, it is carried out at the following stages of pregnancy:
Between weeks 11 and 14, the baby’s gestational age is determined. The structure and function of the placenta are also evaluated (using Doppler ultrasound of the uterine artery).
Between weeks 20 and 22, a morphological ultrasound is performed, during which fetal growth, organ formation, sex, and location of the placenta and umbilical cord are reviewed. In addition, it serves to detect any congenital malformations in time.
Fetal growth, fetal position (head, breech, or transverse), amount of amniotic fluid, and placental integrity are assessed between weeks 32 and 38.