Whiplash Management
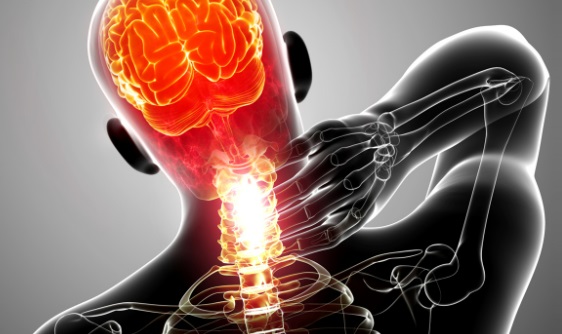
The condition is commonly misunderstood and treated incorrectly. Whiplash is a common injury that can cause neck and shoulder pain, headaches, dizziness, fatigue, arm pain, numbness or weakness, visual disturbances, and ringing (tinnitus) in the ears. In severe cases, the symptoms can include depression, anxiety, anger, frustration, stress, drug dependence, post-traumatic stress, sleep disturbances, sick leave, and lost productivity. The symptoms of a traumatic brain injury can include fatigue, difficulty forming thoughts, and a “mental fog.” If litigation is involved, it can also complicate the case. Some people who are involved in car accidents recover quickly. However, others continue to suffer from symptoms for many years. Chronic pain can be devastating both to the individual and their family.
Whiplash is caused by a rapid “crack of the whip” action that happens before muscles can react (within 300 milliseconds — too fast for our muscles to contract voluntarily). Around halfway through this process, the lower part of the cervical spine extends, and the upper portion flexes. This causes significant pressure to be placed on the disks and joint capsules located in the lower neck. A 2014 study revealed that it may be possible to “trick” the neck muscles to relax before the crash. This would reduce the pressure on neck structures and possibly tissue injuries. Neck muscle contractions are common in rear-end collisions due to a combination of postural and startle reactions. Researchers found that a loud (105dB), 250 milliseconds before impact, tone could reduce the tightness in the neck muscles. They then investigated whether deep, involuntary, stabilizing muscles of the cervical spine (specifically, the multifidus) would also respond to a loud sound. This is important because the muscles are attached directly to the small joints at the back of your spine, and they can increase the strain on the capsules in a crash. Researchers subjected 12 study participants to whiplash simulations with or without loud sounds. The researchers’ results indicate that a loud tone before impact may reduce strain on the facet joints of the cervical spine, which may, in turn, reduce tissue injuries during a rear-end collision. These findings are very exciting, as they may reduce the severity of injuries caused by using this tone before an impact.
Exercises and care that promote range of motion early on appear to be more effective than using a cervical collar or rest. Manual therapies such as early manipulation, mobilization, and traction, along with soft tissue therapy, have been shown to improve outcomes in whiplash patients. Chiropractic provides these treatments to whiplash victims more often than other healthcare professionals. Chiropractic doctors also provide patient education on proper posture, bending, pulling, and pushing techniques, and the use of heat over ice (especially at first). They may also suggest home-based treatments and self-care. Exercises often include range-of-motion/stretching, cervical curve retraining, strengthening, stabilization exercises, and balance exercises. Your chiropractor can help you manage dizziness by showing you specific exercises.
This article was written by an Auto Injury Doctor at Florida Medical Pain Management. Florida Medical Pain Management is proud to offer comprehensive pain management services to a diverse group of patients. Patients at Florida Medical Pain Management can get help managing hip, knee, leg, and neck pain. The practice also offers comprehensive arthritis management, along with treatments for auto accidents, sports, and work injuries.